We boost citizen science technologies
Cos4Cloud addresses one of the biggest challenges of citizen science: the quantity and quality of data, as well as maintaining the citizen observatories used to collect this data.
Project Overview
Cos4Cloud (Co-designed citizen observatories for the EOS-Cloud) is a European Horizon 2020 project to boost citizen science technologies.
One of the biggest challenges of citizen science is the quality of data, as well as maintaining the citizen observatories used to collect this data. Cos4Cloud is addressing these challenges by developing thirteen technological services to improve citizen science platforms, also known as citizen observatories, to help them boost the quantity and the quality of observations and, finally, to help ensure their long-term viability.
The services will be co-designed with key stakeholders and carefully tested with end-users
Cos4Cloud relies on the participation of a network of 9 citizen observatories and Do it Yourself (DIY) initiatives focused on biodiversity and environmental monitoring.
These platforms will be responsible for testing the various services with their users. Four of the largest citizen biodiversity observatories in Europe will collaborate in the first part of the project: Natusfera, iSpot, Pl@ntNet and Artportalen.
In the second part, the services will be tested on platforms focused on environmental monitoring in water (Freshwater Watch and KdUINO) and air: odours (OdourCollect), particular matter (CanAir.io) and aerosols (iSpex).
The project will organize a wide range of activities.
From BioBlitzes to Datathons and Hackathons, as well as creating a space to exchange knowledge and share best practices.
These activities will be a useful space for encouraging citizen observatories to work together, especially on common challenges regarding infrastructure and technology.
Cos4Cloud is an opportunity for networking among citizen observatories and an invitation to search for collective solutions for their sustainability.
Objectives
Our core mission is to improve citizen observatories technologies to help them increase the quantity and the quality of observations and, finally, to help ensure their long-term viability.
Collaborate on international and interdisciplinary levels
Facilitate networking and knowledge-management processes across organizations, people and initiatives working on citizen observatories.
Help citizen observatories’ sustainability
Help ensure the long-term viability of citizen science platforms.
More and better data
External cloud-based services will ensure collection of larger data sets with improved quality control.
Support citizen science growth
Integrate citizen science into the European Open Science Cloud to make it available to the whole scientific community.
Develop innovative technologies
Make available technological services built by and for users that improve the citizen observatories and contribute to their sustainability.
Increase the use of citizen science data
Follow the FAIR data principles (findable, accessible, interoperable and reusable) to make the most of the data available from citizen science.
EOSC
The European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) is developing a large virtual infrastructure to support and develop open science and open innovation in Europe and beyond. Specifically, it is a virtual environment for the whole scientific community to store, manage, analyse and re-use data for research, innovation and educational purposes, which aims to:
Integrate
and consolidate e-infrastructure platforms
Federate
existing research infrastructures and science clouds.
Support
the development of cloud-based services for open science
The creation of the EOSC is one of the eight priorities of the European Open Science Agenda, along with promoting citizen science. There is a need, then, to integrate citizen science into the EOSC digital ecosystem, so that citizen science grows and adds value to the EOSC community.
We are pioneer in integrating citizen science in the EOSC
The ten services developed by Cos4Cloud will be uploaded to the EOSC as modules, so that any existing citizen science observatory can select and install the technological services needed to improve its functionalities.
Minimum viable ecosystem
The basic set of services in the EOSC ecosystem is called the Minimum Viable Ecosystem (MVE). Consolidation of this MVE requires basic technical, political, and human conditions.
Interoperable services and open data, a coordinated effort to put the right incentives in place for all those involved (researchers, software developers, infrastructure managers, research managers and users) are some of these conditions (European Commission, 2018).
The MVE for citizen observatories proposed by Cos4Cloud consists of a co-designed and prototyped set of services to tackle the challenges facing citizen observatories and will take into account the following priorities:
Co-designed with key stakeholders
Standardised data-models to increase interoperability capabilities
Modular software ecosystem around citizen-science knowledge representation
Focus on the final user and the potential impact of the citizen science
Artificial intelligence, data quality and reputation-assessment
Personalised notification systems
Data-use notification and user experience maximisation
Integration of data from biodiversity and environmental quality
Knowledge transfer and linguistic tools
Minimum viable ecosystem as an opportunity for tackling citizen science challenges
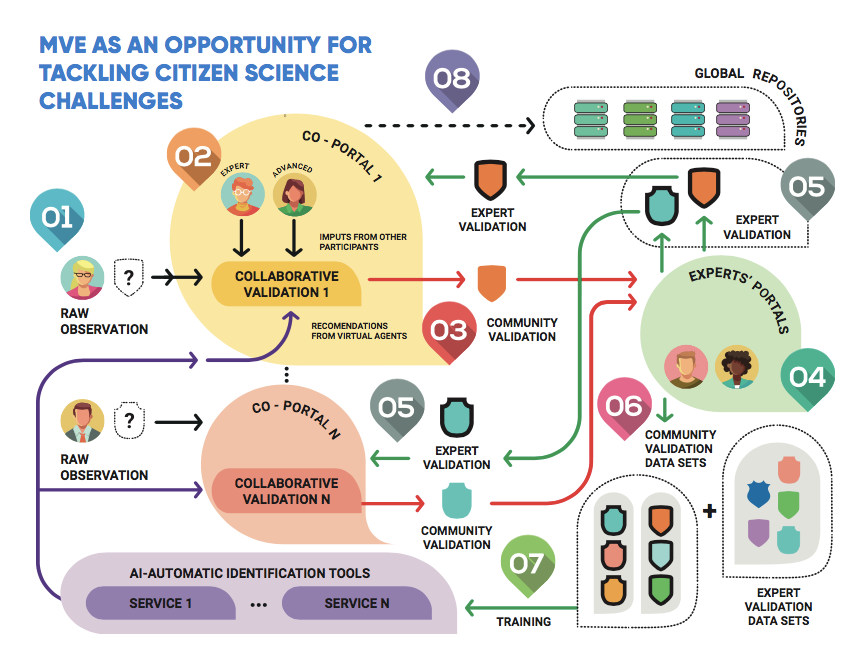
Cos4Cloud will create a MVE where the citizen observatories, technological services, citizen science experts validating data and users are able to establish synergies and collaborate to generate high-quality data in global repositories.